|
>US/AZ Government
>World History
>Nogales High School Web Page
Class stuff...
>A letter to
my students
>Course Guide
in PDF
>Photos of Old
Nogales
>Socratic
Seminar
Grading
>The
Habits
of Mind, Heart and Effectiveness
>Position
Papers
Constitution Info
>The
Founders' Constitution
>The
Federalist
Papers
>Constitution Basics
>The Constitution
Society
>Arizona Legislature
>Alexis de Tocqueville, Democracy in America
|
Fundamentals Economics
|
Economics
Rationale
-- From AZ Social Studies Standards
The goal of the economics strand is to enable students to make reasoned
judgments about both personal economic questions and broader questions
of economic policy. Students will develop an economic way of
thinking and problem solving to understand and apply basic economic
principles to decisions they will make as consumers, members of the
workforce, citizens, voters, and participants in a global
marketplace. This will prepare students to weigh both short-term
and long-term effects of decisions as well as possible unintended
consequences. The study of economics explains historical developments
and patterns, the results of trade, and the distribution of income and
wealth in local, regional, national, and world economies.
Students will be able to analyze current issues and public policies and
to understand the complex relationships among economic, political, and
cultural systems.
|
|
Concept 1: Foundations of
Economics
The foundations of economics are the application
of basic economic concepts and decision-making skills. This
includes scarcity and the different methods of allocation of goods and
services.
|
1.4 and 1.5.10
|
- Senior Project Planning
- The Bailout
- Intro to Keynes and Friedman
-
Econ Unit Intro. Text review
- Scarcity
- The three questions
- Economics - a study
- Review Economics Rationale --
From AZ Social Studies Standards
Review
Econ Strands and Concepts required by Arizona
- Record and calculate what you send in one day. How does this reflect your demand?
- Students copy these concepts into notes
Define and
discuss:
- Basic Economic Problem
- Scarcity
- The three questions
- Economics - a study
- The factors of production
- Opportunity Costs
- Production Possibilities
- Circular flow
|
|
1.6.10
|
|
The
Seven
Principles
of
the
Economic
Way
of Thinking and Reasoning
It's all about
individual choice - Luck has nothing to do with it; marginal analysis
... everything.
1.
People choose.
2. People’s choices involve costs.
3. People respond to incentives in predictable ways.
4. People create economic systems that influence individual
choices and incentives.
5. People gain when they trade voluntarily.
6. People’s choices have consequences that lie in the future.
7. The laws of Supply and
Demand affect every aspect of life.
|
|
1. 7 and 1.8
|
- Econ Vocab Foldable make it in-class
- Read Chapter 1
- Define and discuss:
- Opportunity Costs
- Production Possibilities
- Circular flow
- Econ Article Review
- Economic way of thinking
- Marginal analysis
- Basic Economic Problem
- Scarcity
- The three questions
- Economics - a study
- The factors of production
|
1.11
|
"Macroeconomics"
activity |
1.12 and 1.13
|
- "GREED" by John Stossel
- "Enlightened Self-Interest"
|
| 1.14 |
Wall Paper Review
- Opportunity Costs
- Production Possibilities
- Circular flow
- Econ Article Review
- Economic way of thinking
- Marginal analysis
- Basic Economic Problem
- Scarcity
- The three questions
- Economics - a study
- The factors of production
- Basic Economic Problem
- Scarcity
- The three questions
- Economics - a study
- The factors of production
|
| 1.15 |
- Written
Vocab
QZ
- e Journal to Nicenet with an answer to
these questions in a few sentences. Both due 1.19.10
- What are the economic
implications of living on the border?
- What is something that is in demand and how can you supply it?
|
1.18
|
|
1.19
|
- Read Econ Text Chapter 2 & 3
- Position Paper work day or Exam work day and
explanation
|
1.20
|
- "Sound of Freedom" video
- React to video
|
1.21 and 1.22
|
- Read Econ Chs. 2/3
- In-class discussion
-
PO 3. Describe the characteristics of the mixed-market economy of the United States:
a. property rights
b. profit motive
c. consumer sovereignty
d. competition
e. role of the government
f. rational self-interest
g. invisible hand
|
| 1.25 |
- Econ Chs 2 and 3 Vocab Foldable made in-class
- collect foldable
- Minimum
Wage
Position Paper due 1.24.10 at nicenet.org
|
1.26 and 1.27
|
- Vocab Quiz from foldable
- Impact of Minimum Wage
- Econ Article Review
- Practice Econ Quiz
- Economic Freedom
- WEW
- Economic Freedom and the Constitution
- Econ Systems
Worksheet
-
Big 40 pt eJounal due
- Read Read
Economics
101
by Walter E. Williams
- Read Econ text book page 381
- Briefly review the ideas
Walter E. Williams.
Say who he is,
Why he's at my web page (teachweb.org).
- Summarize his main point about "economic freedom"
Concept 1 - PO 4.
Evaluate
the economic implications of current events from a variety of
sources (e.g., magazine articles, newspaper articles, radio, television
reports, editorials, Internet sites). |
| 1.28 and 1.29 |
- "The Power of
Ideas...Milton Friedman...Economist" Video
- Chs 1,2 and 3 exam due by 2.2.10
|
| 2.1.10 |
- Keynes vs Freidman
- "The Pencil" Video
|
| 2.2.10 |
Concept 2: Microeconomics
Microeconomics examines the costs and benefits of
economic choices relating to individuals, markets and industries, and
governmental policies.
PO 2. Describe how markets
function:
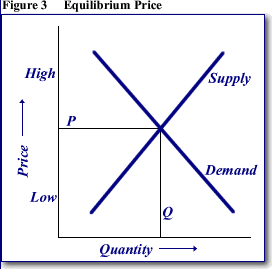
a. laws of supply and demand
b. how a market price is determined
c. graphs that demonstrate changes in supply and demand
d. how price ceilings and floors cause shortages or surpluses
e. comparison of monopolistic and competitive behaviors
f. theory of production and the role of cost
- READ CHAPTER 4 - DEMAND
- Lecture Supply and demand
- Vocab review
|
| 2.3 |
- Lecture Ch 4 Demand
- Essay assignment-"What
will you do when gas hits 5$ per gallon?"
4SS-P2.
- Read chapter 4 at home
- An
excellent supply and demand web site
QuickWrite on article in-class on one section
|
| 2.4 |
- Vocab Quiz from foldable
- collect foldable
|
| 2.5 |
Concept 2 - Microeconomics
PO 2. Describe how markets
function:
a. laws of supply and demand
b. how a market price is determined
c. graphs that demonstrate changes in supply and demand
d. how price ceilings and floors cause shortages or
surpluses
e. comparison of monopolistic and competitive behaviors
f. theory of production and the role of cost
|
| 2.8 |
- EconCh 5 lecture Supply
- Group
Reports on Economists and Economic Concepts
Economists/Entrepreneur Reports
|
| 2.9 |
- Chapter 6 lecture - Prices
- You own a restaurant that is fully booked during the
weekends. In mid-week, however, you rarely have enough bookings to stay
open. To make more money during this slow period, you decide to cut
dinner prices by one-third- from $15 to $10 – on Wednesday and
Thursday.Do you think this action will increase your revenues?
Explain why or why not.
Explain, give two examples, connect to the principle
of elasticity of demand .
or
2. You have a friend that is diabetic that must take
insulin daily. In the last year he cost of insulin has doubled. Using
the principle of demand elasticity, explain you friend's choices.
|
| 2.10 |
- Exam Econ Chapters 4, 5 and 6 due by 2/13
- Exam Review
- Econ Ch. 6 - Vocab Quiz
|
2.11 to 2.13
|
|
2.13
|
Economist group reports
|
AZ State Standards covered:
Concept 1: Foundations of Economics
PO 1. Analyze the implications of
scarcity:
- limited resources and unlimited human wants influence
choice at individual, national, and international levels
- factors of production (e.g., natural, human, and
capital resources, entrepreneurship, and technology)
- marginal analysis by producers, consumers, savers,
and investors
PO 2. Analyze production possibilities
curves to describe opportunity costs and
trade-offs.
PO 3. Describe the characteristics of
the mixed-market economy of the United States:
- property rights
- profit motive
- consumer sovereignty
- competition
- role of the government
- rational self-interest
- invisible hand
PO 4. Evaluate the economic
implications of current events from a variety of sources (e.g.,
magazine articles, newspaper articles, radio, television reports,
editorials, Internet sites).
PO 5. Interpret economic information using
charts, tables, graphs, equations and diagrams.
Concept 2 - Microeconomics
PO 1. Describe how the interdependence
of both households and firms is affected by trade, exchange, money, and
banking:
a. why voluntary exchange occurs only when all
participating parties expect to gain from the exchange
PO 2. Describe how markets function:
a. laws of supply and demand
b. how a market price is determined
c. graphs that demonstrate changes in supply and demand
d. how price ceilings and floors cause shortages or
surpluses
e. comparison of monopolistic and competitive behaviors
f. theory of production and the role of cost
PO 4. Evaluate the economic
implications of current events from a variety of sources (e.g.,
magazine articles, newspaper articles, radio, television reports,
editorials, Internet sites).
PO 5. Interpret economic information using
charts, tables, graphs, equations and diagrams.
Concept 2 - Microeconomics
PO 1. Describe how the interdependence
of both households and firms is affected by trade, exchange, money, and
banking:
a. why voluntary exchange occurs only when all
participating parties expect to gain from the exchange
PO 2. Describe how markets function:
a. laws of supply and demand
b. how a market price is determined
c. graphs that demonstrate changes in supply and demand
d. how price ceilings and floors cause shortages or
surpluses
e. comparison of monopolistic and competitive behaviors
f. theory of production and the role of cost
|